

Hemodynamic orthostatic dizziness/vertigo: Diagnostic criteria. National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Diseases (NIDCD). Lightheadedness can be a side effect of medications. This condition often accompanies anxiety disorders and may cause lightheadedness.
Abnormally rapid breathing (hyperventilation). Depression (major depressive disorder), anxiety and other psychiatric disorders can cause dizziness. Abnormalities of the vestibular system can lead to a sensation of floating or other false sensation of motion. These include cervical spondylosis and Parkinson's disease.Ī sense of dizziness or lightheadedness can result from: Loss of balance or unsteadiness can be a side effect of medications. Difficulties with eyesight also can lead to unsteadiness. Muscle weakness and unstable joints can contribute to your loss of balance. The damage can lead to difficulties with walking. Nerve damage to your legs (peripheral neuropathy). Abnormalities in your inner ear can cause a sensation of a floating or heavy head and unsteadiness in the dark. Losing your balance while walking, or feeling imbalanced, can result from: Abnormal heart rhythms (heart arrhythmia), narrowed or blocked blood vessels, a thickened heart muscle (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy), or a decrease in blood volume can reduce blood flow and cause lightheadedness or a fainting feeling. Standing or sitting up too quickly can cause some people to experience a significant drop in their blood pressure, resulting in feeling lightheaded or faint. Hemodynamic orthostatic hypotension (postural hypotension). Motion sickness is common in people with migraines. You might experience dizziness in boats, cars and airplanes, or on amusement park rides. You might experience vertigo due to a concussion or other head injury. You might experience vertigo, ear pain, facial weakness and hearing loss. Also known as herpes zoster oticus, this condition occurs when a shingles-like infection affects the facial, auditory and vestibular nerves near one of your ears. You might experience dizziness or loss of balance, but the most common symptoms are hearing loss and ringing in your ear. This noncancerous (benign), slow-growing tumor develops on a nerve that affects your hearing and balance. Dizziness and sensitivity to motion (vestibular migraine) can occur due to migraine. Meniere's disease is rare and typically develops in people who are between the ages of 20 and 40. The cause of Meniere's disease isn't fully known. In addition to sudden and severe vertigo, Meniere's disease can cause fluctuating hearing loss and buzzing, ringing or a feeling of fullness in your ear. This is the third most common disorder in adults. Symptoms often worsen when you watch objects move, when you read or when you are in a visually complex environment such as a shopping mall. Symptoms include unsteadiness or a sensation of motion in your head. This disorder occurs frequently with other types of vertigo. Persistent postural-perceptual dizziness. 
This is a common disorder second to BPPV in adults. Symptoms can last several days and gradually improve without treatment. Symptoms are often severe and persistent, and include nausea and difficulty walking. This inflammatory disorder, probably caused by a virus, can affect the nerves in the balance portion of your inner ear. You might experience a spinning sensation when turning in bed or tilting your head back to look up. BPPV is the most common cause of vertigo in adults. BPPV occurs when calcium crystals in your inner ear - which help control your balance - are dislodged from their normal positions and move elsewhere in the inner ear. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).Vertigo can be associated with many conditions, including:
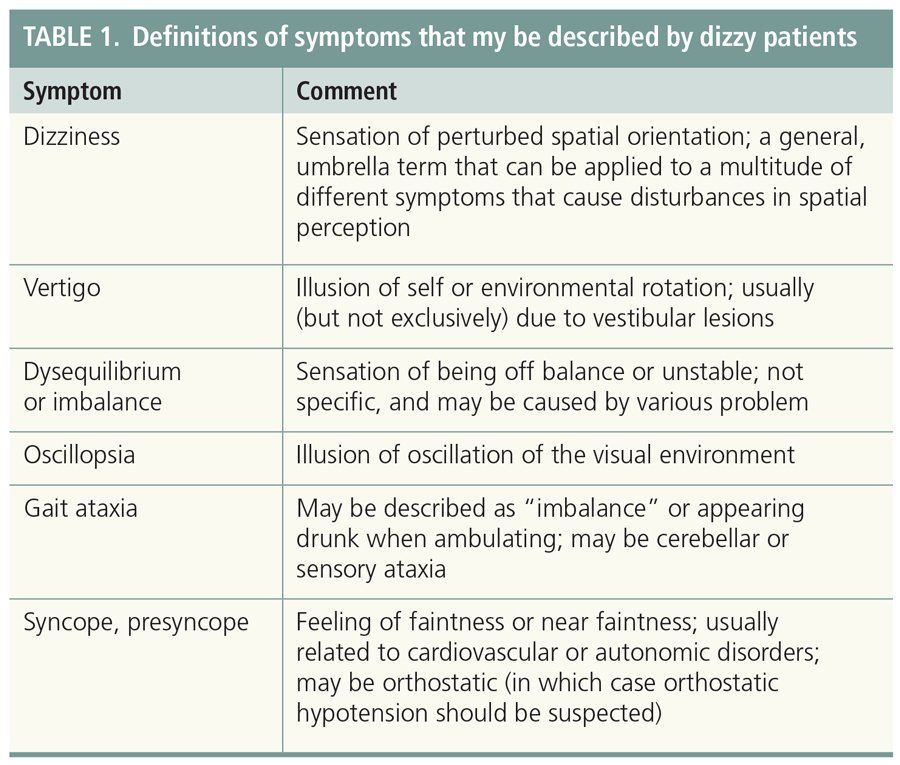
The cause of balance problems is usually related to the specific sign or symptom. Balance problems can be caused by several different conditions.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
